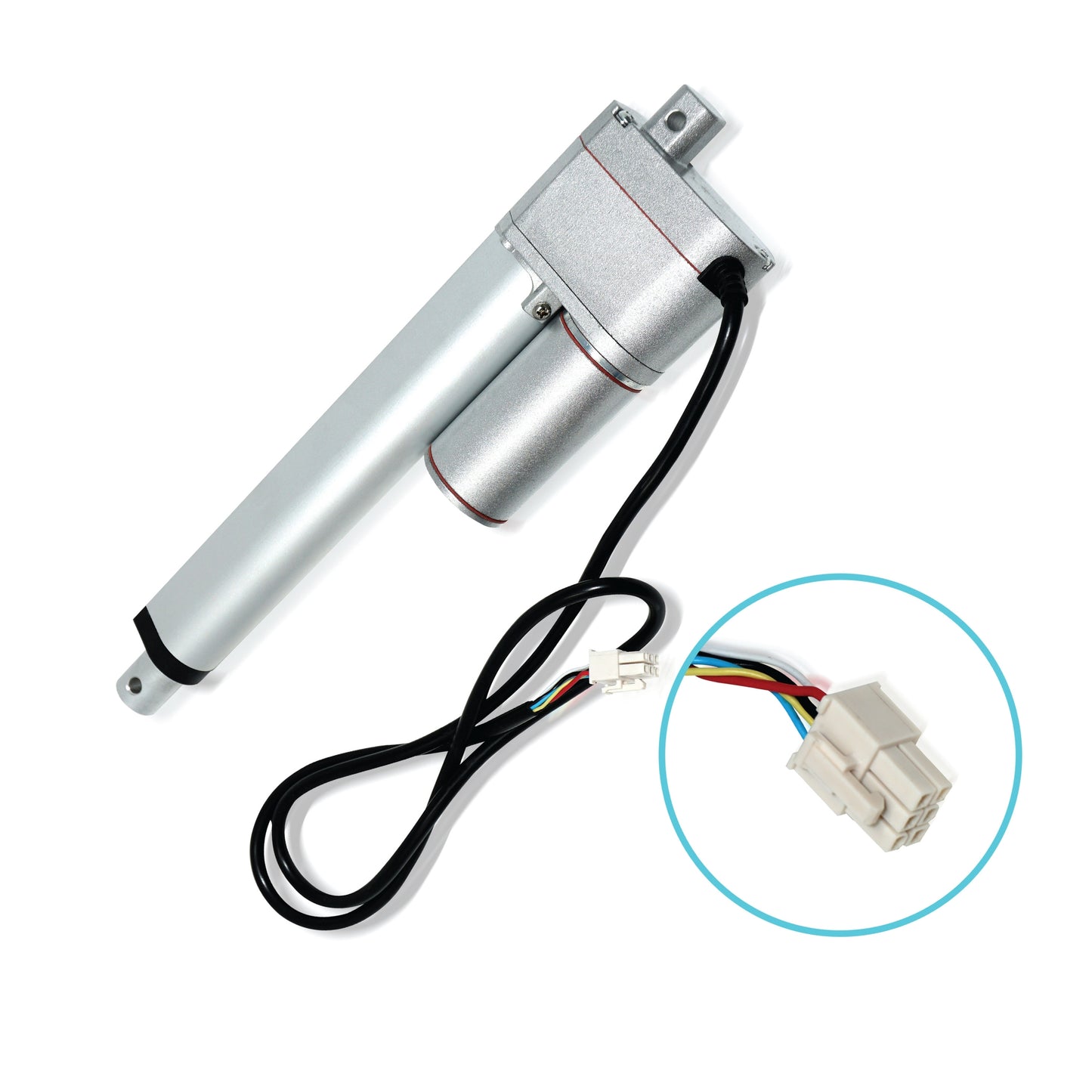
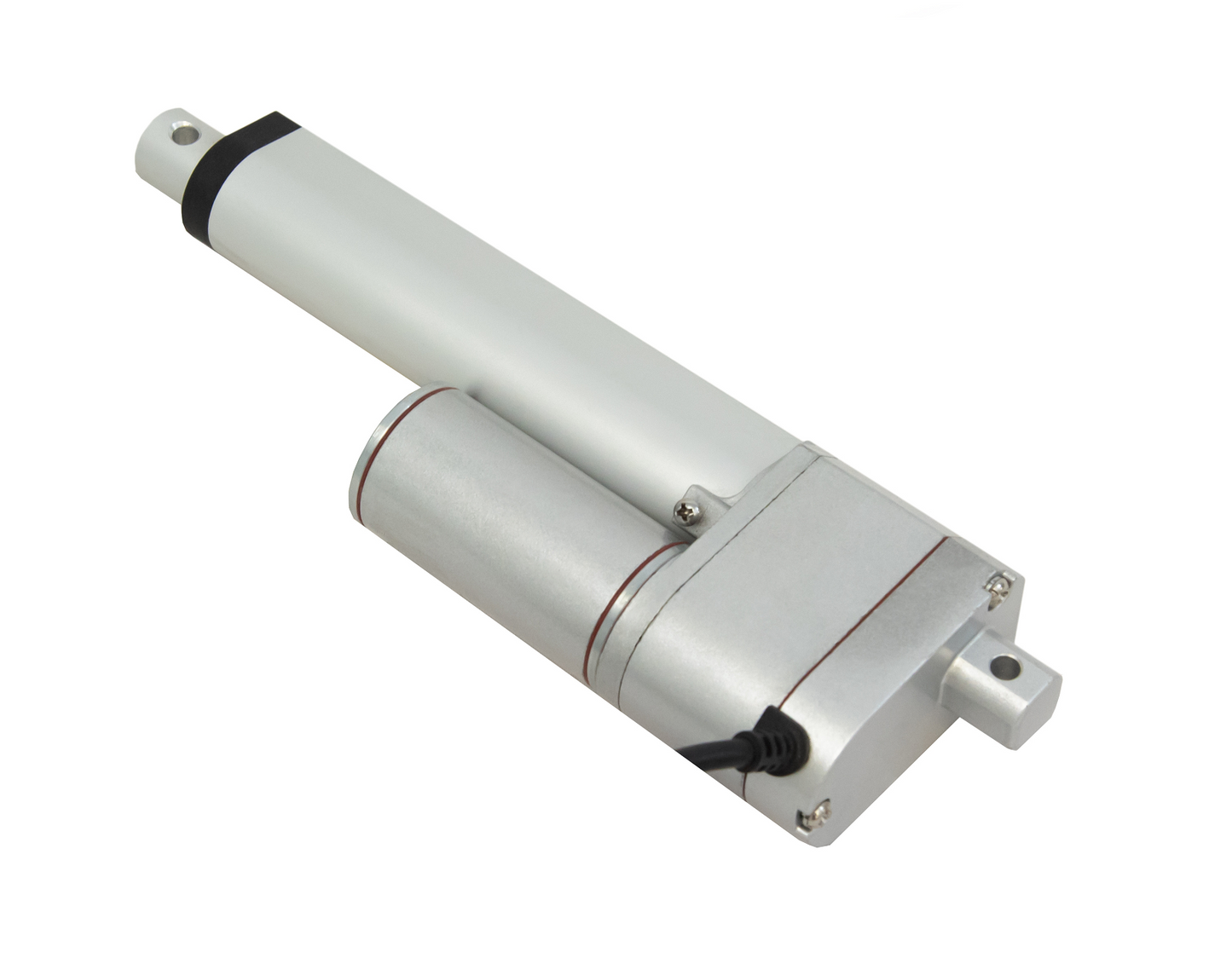
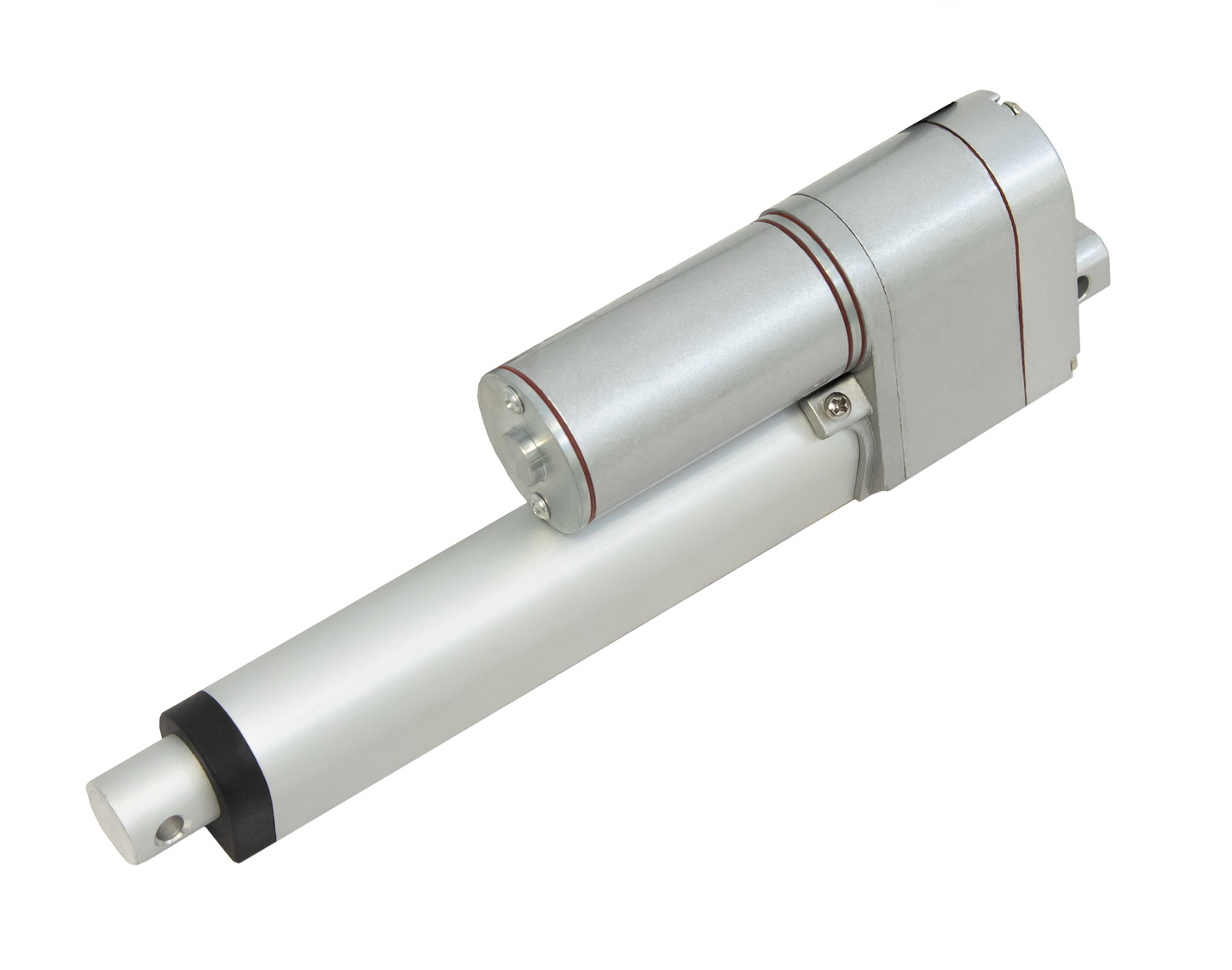
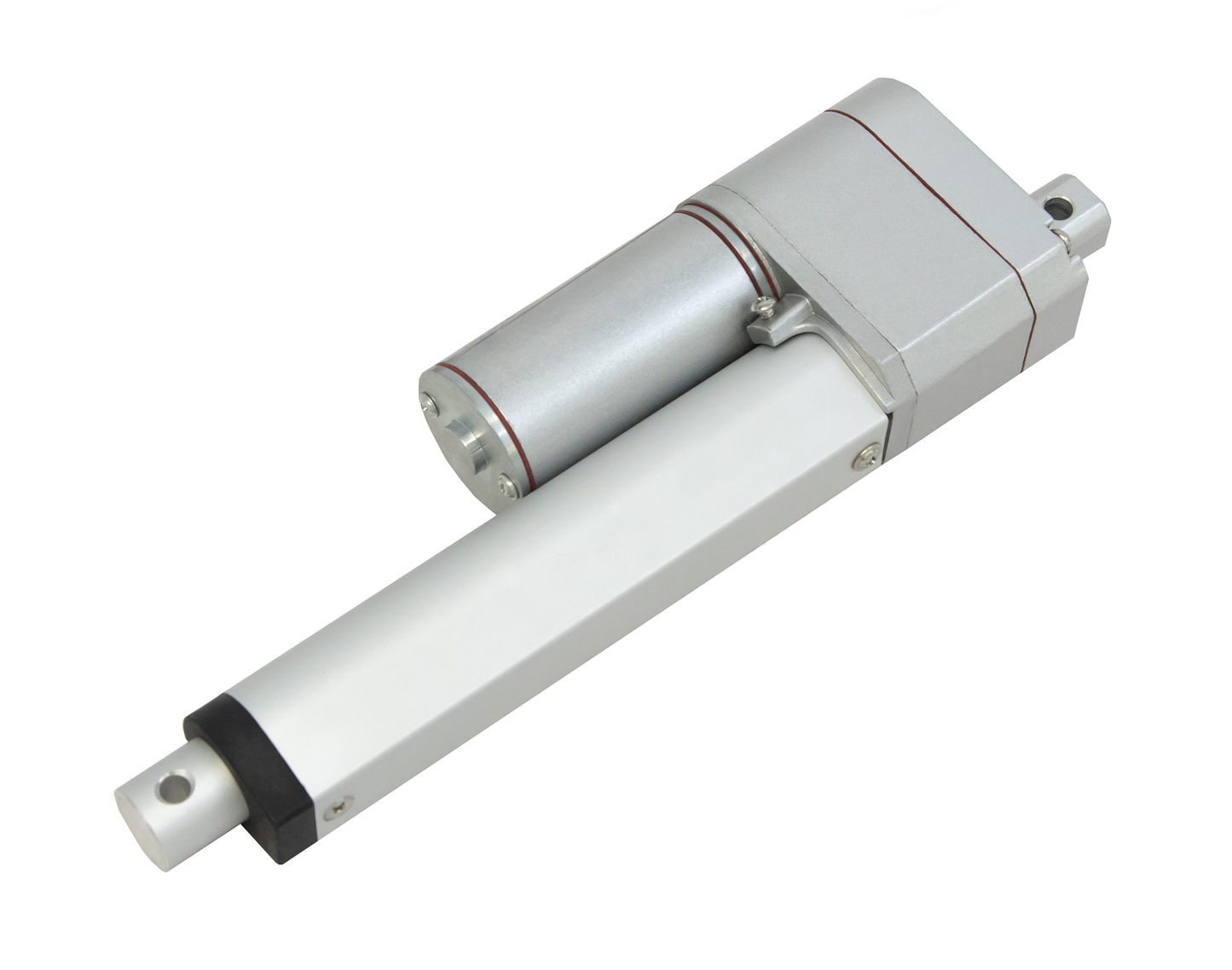
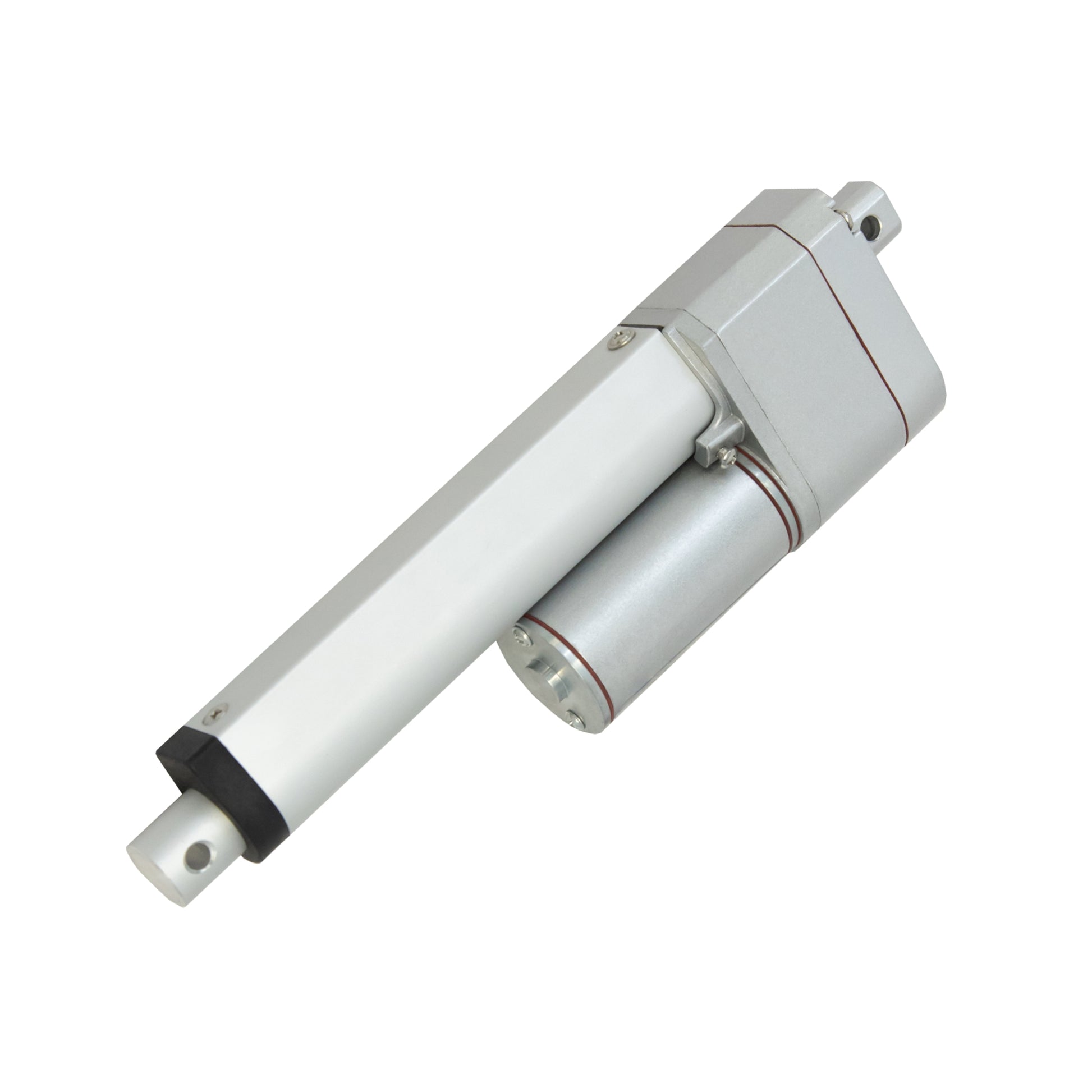
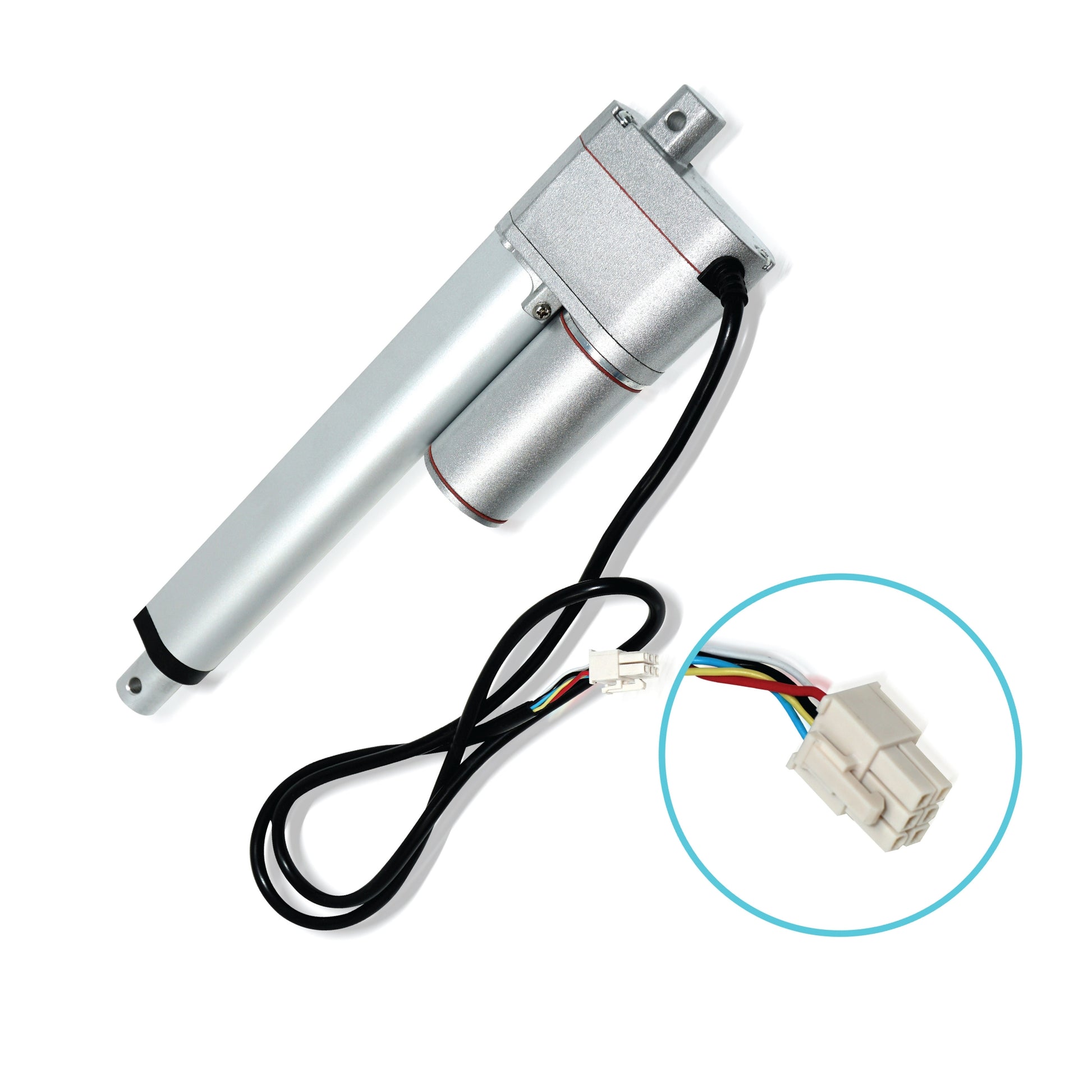
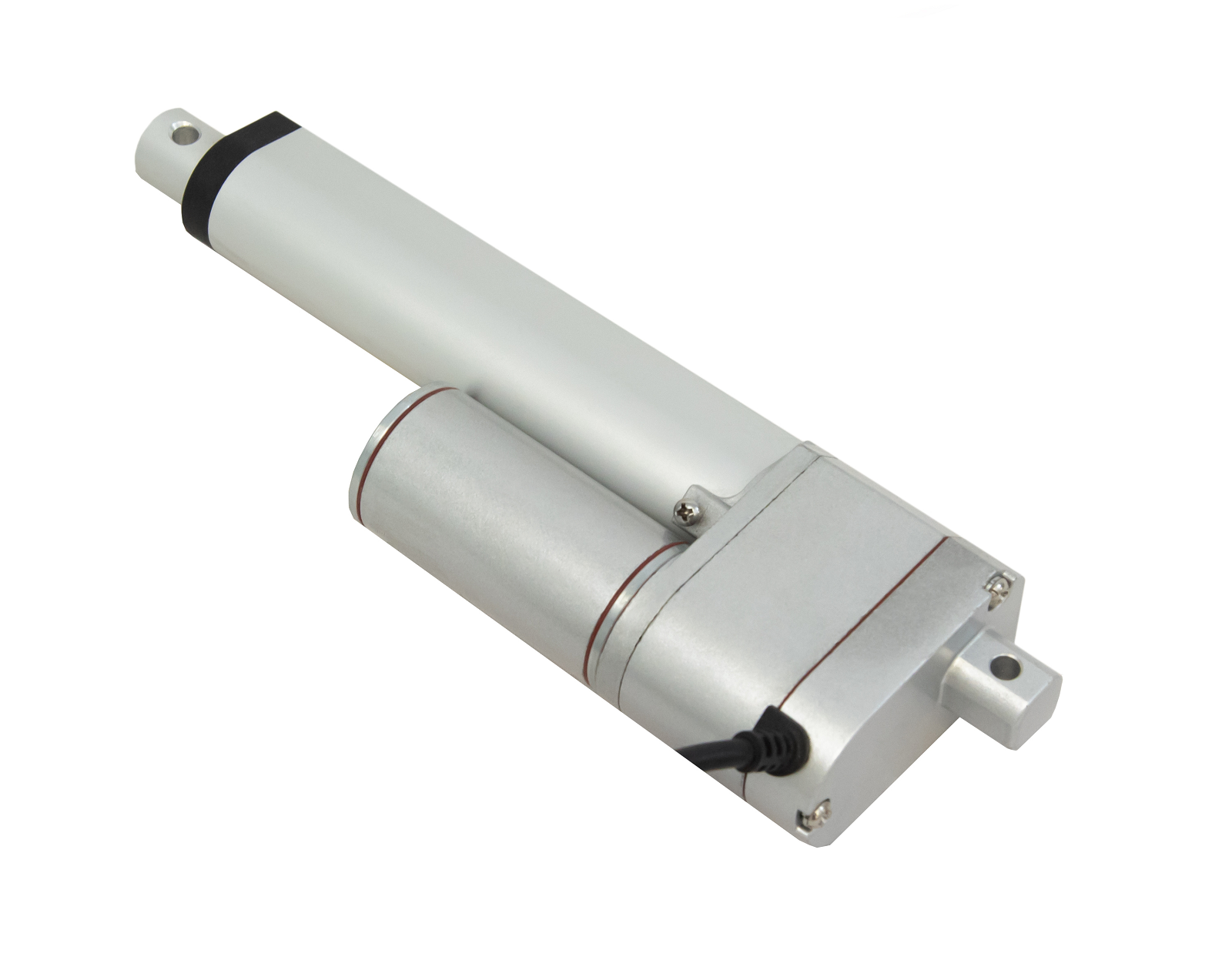
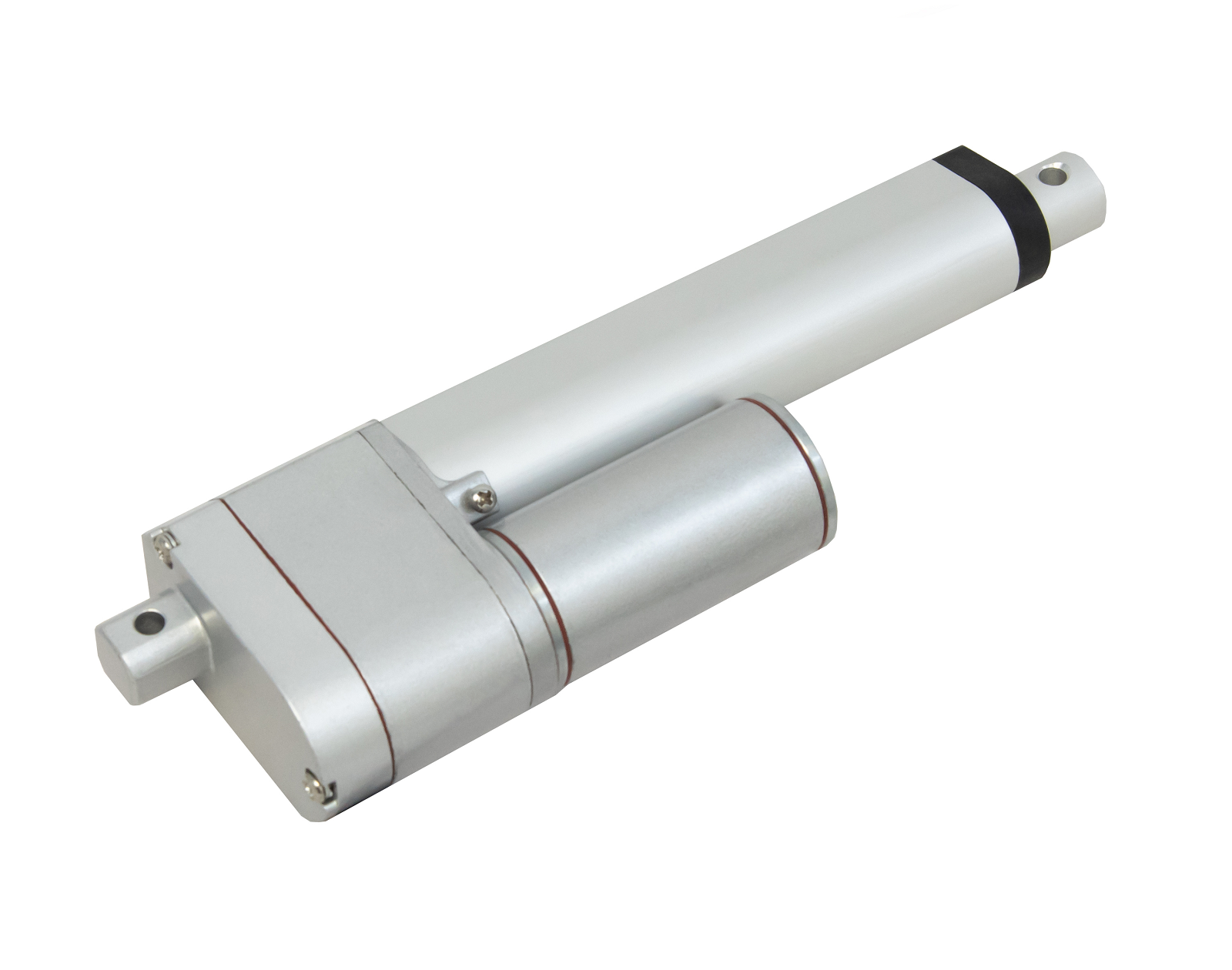
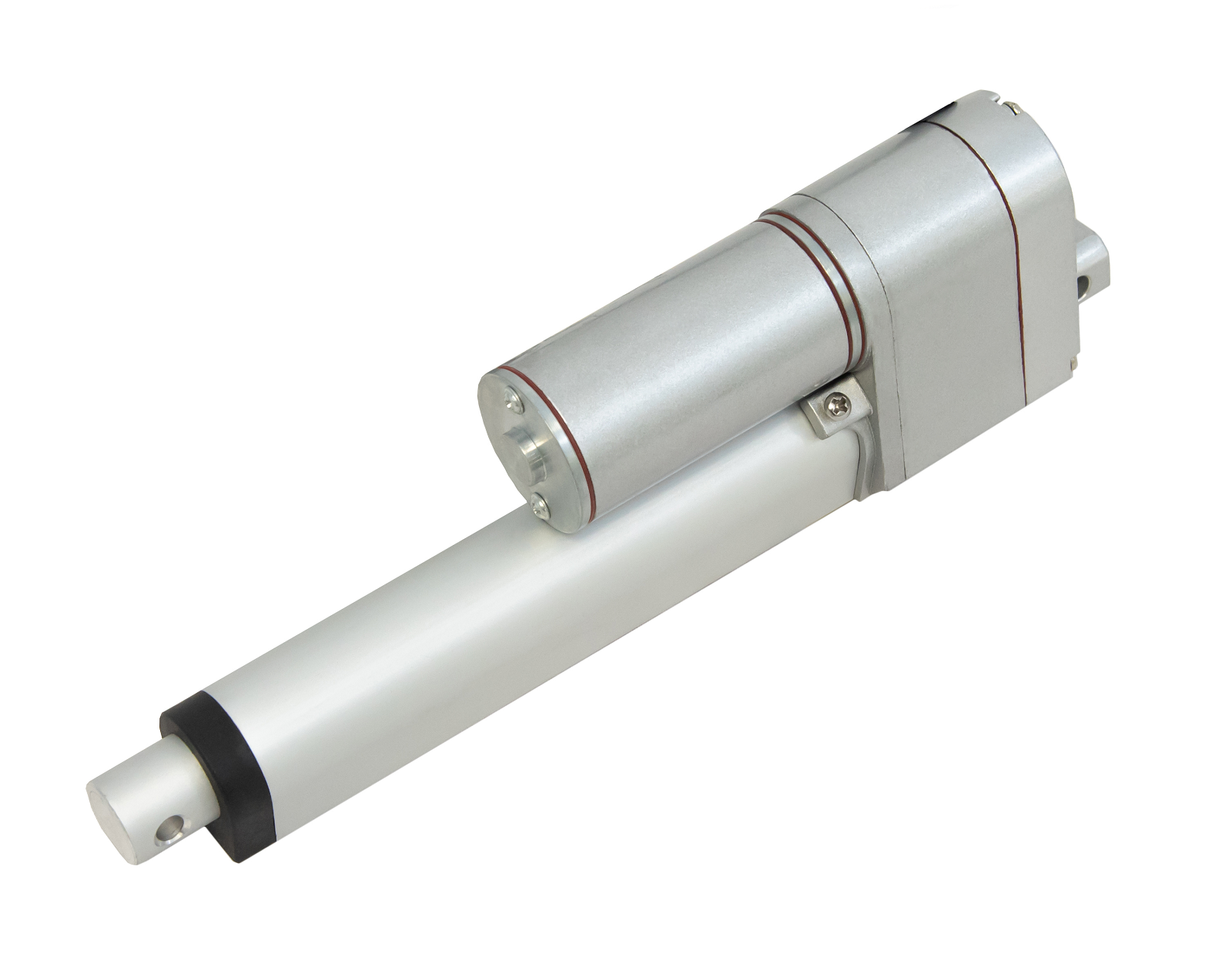
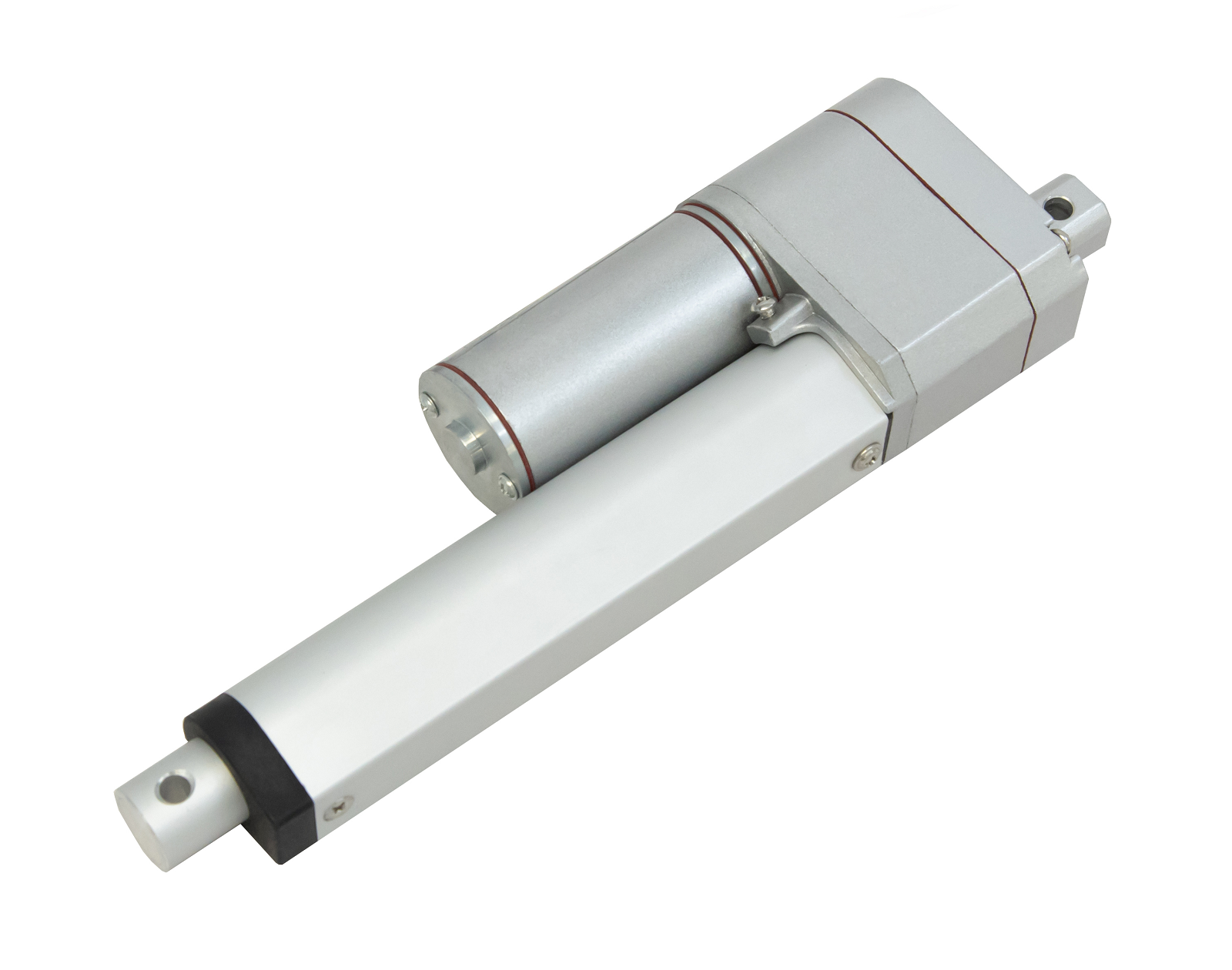
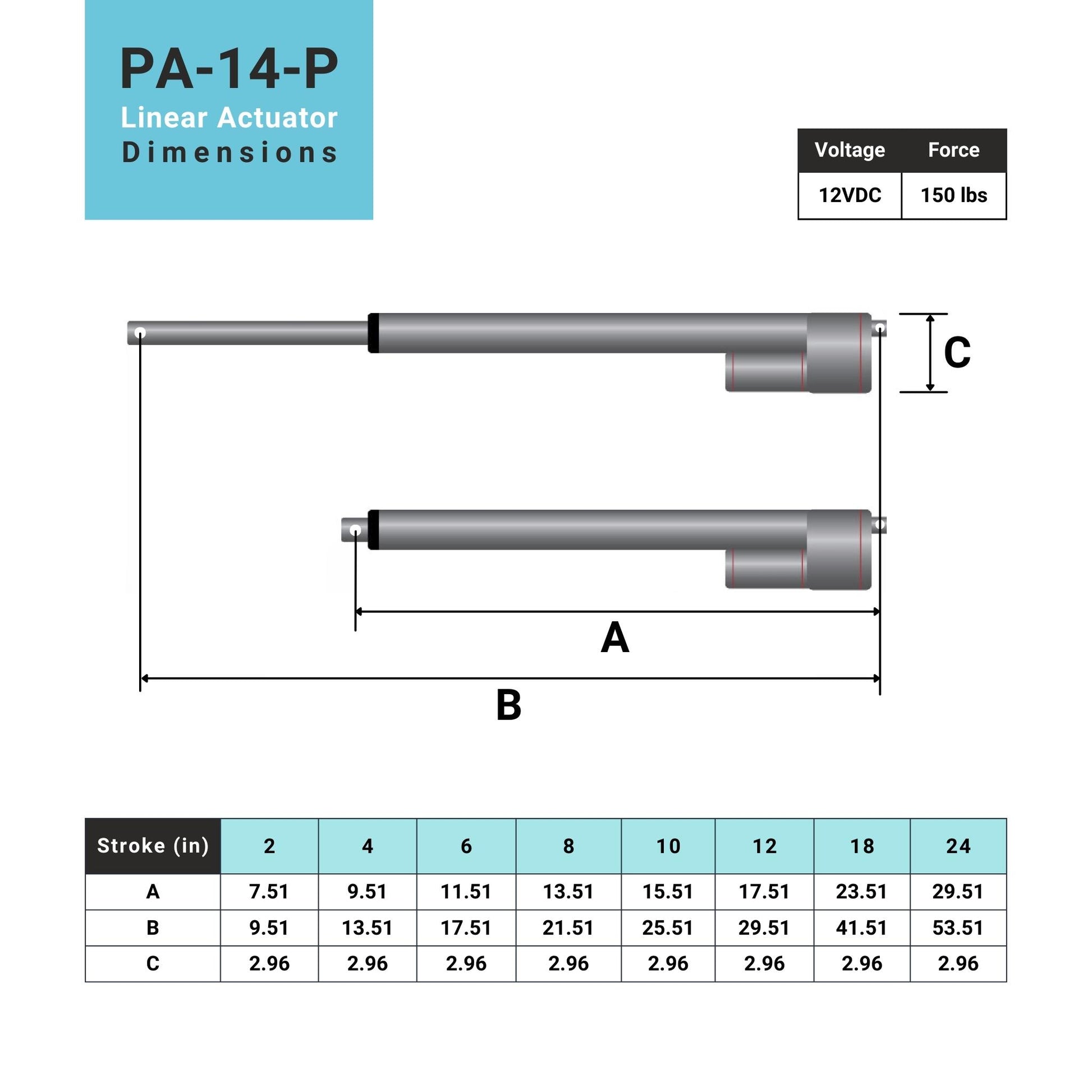
L'actionneur linéaire à rétroaction PA-14P utilise un concept de mouvement linéaire dans un caisson compact. Le retour de potentiomètre intégré permet la commande de la position. Cette fonctionnalité est importante pour les applications qui nécessitent de la précision. L'actionneur à faible courant et à force moyenne est idéal pour l'automatisation, l'ébénisterie, l'agriculture et la robotique.
Pour une liste complète des spécifications, des options de personnalisation et des dessins dimensionnels, veuillez consulter notre fiche technique PA-14P.
OPTIONS DE FIXATION :
Le support BRK-14 est conçu pour cet actionneur linéaire 12v et permet un processus d'installation simple. Pour des informations et des spécifications plus détaillées, veuillez consulter notre page de produits de supports.
SYSTÈMES DE COMMANDE:
La faible consommation de courant PA-14P permet une connectivité avec la plupart de nos systèmes de commande. Pour plus d'informations sur nos boîtiers de commande plug-n-play et nos micro-contrôleurs, veuillez consulter notre page sur les systèmes de commande.
* Nos actionneurs PA-14P sont compatibles avec les boîtiers de commande PA-39 pour la possibilité d'enregistrer 3 emplacements prédéfinis, de contrôler les actionneurs linéaires en mouvement séquentiel et d'étendre, d'arrêter et de rétracter le mouvement. Pour plus d'informations, veuillez contacter sales@progressiveautomations.com.
Tableau de comparaison des actionneursOptions sur mesure
Vous recherchez un actionneur mais les spécifications ne correspondent pas exactement à ce dont vous avez besoin ? Nous avons une longue liste de capacités pouvant être faites sur mesure pour vous assurer d'obtenir exactement ce dont vous avez besoin pour votre projet. Téléchargez la fiche technique de ce produit et découvrez vos options sur mesure !
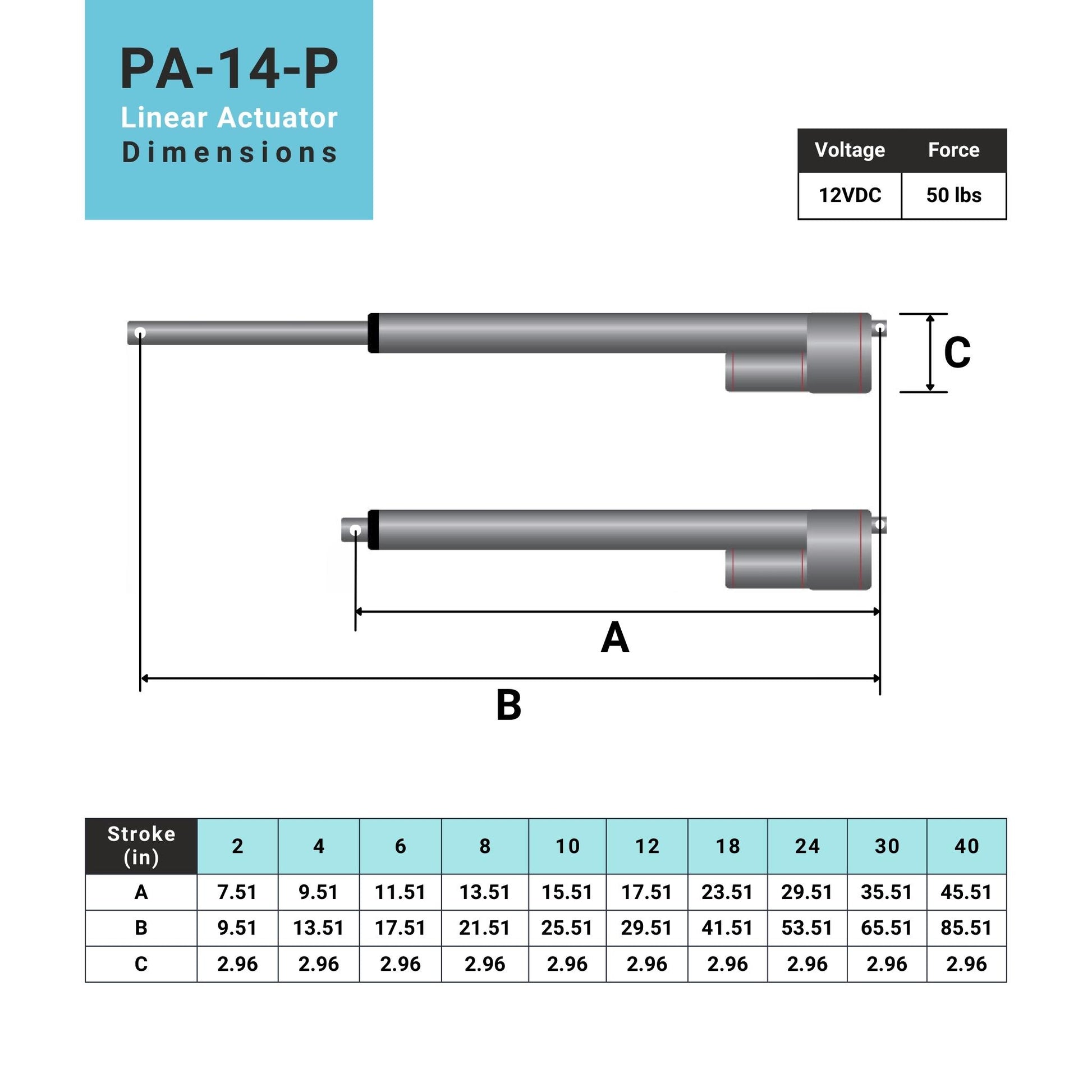
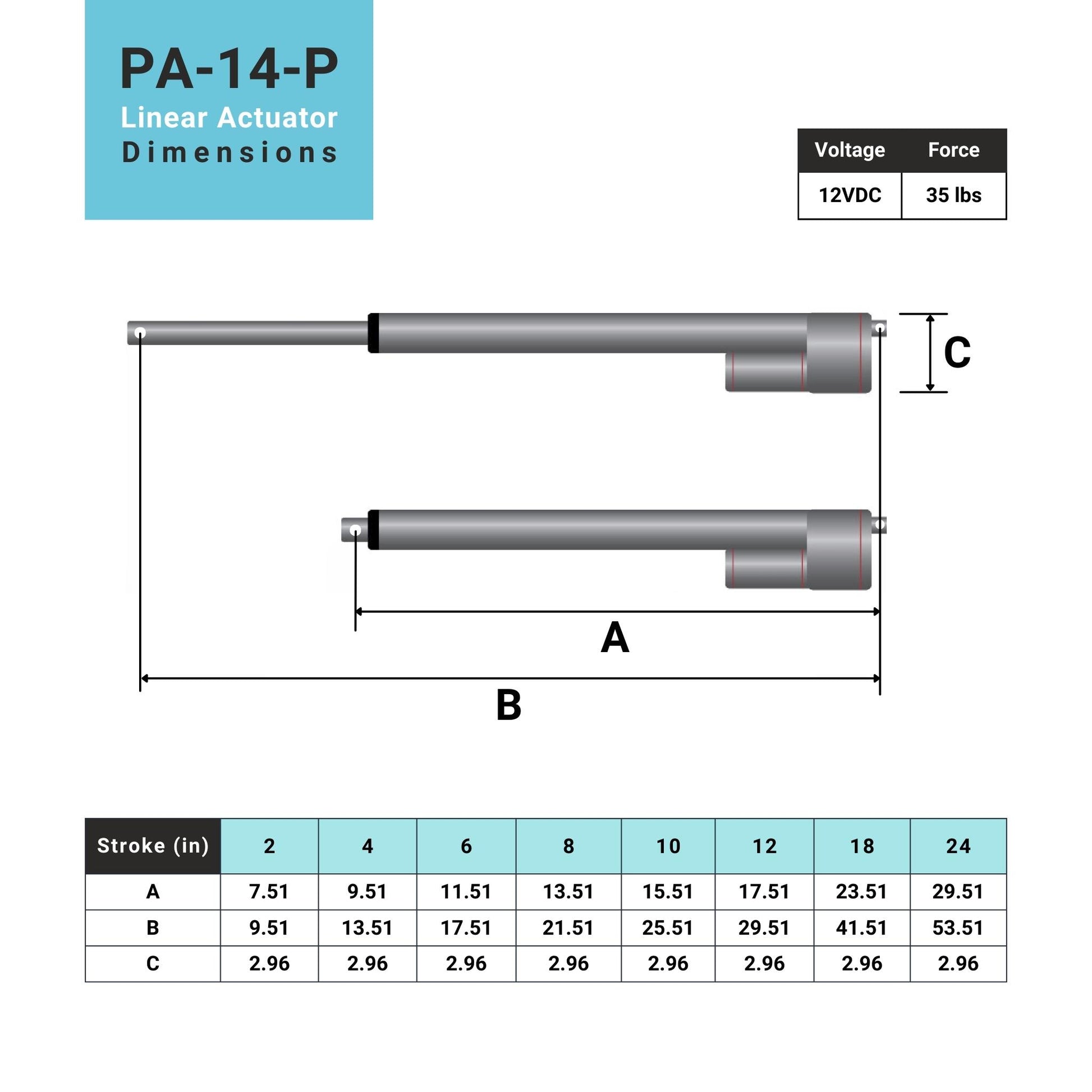
L'actionneur linéaire à rétroaction PA-14P utilise un concept de mouvement linéaire dans un caisson compact. Le retour de potentiomètre intégré permet la commande de la position. Cette fonctionnalité est importante pour les applications qui nécessitent de la précision. L'actionneur à faible courant et à force moyenne est idéal pour l'automatisation, l'ébénisterie, l'agriculture et la robotique.
Pour une liste complète des spécifications, des options de personnalisation et des dessins dimensionnels, veuillez consulter notre fiche technique PA-14P.
OPTIONS DE FIXATION :
Le support BRK-14 est conçu pour cet actionneur linéaire 12v et permet un processus d'installation simple. Pour des informations et des spécifications plus détaillées, veuillez consulter notre page de produits de supports.
SYSTÈMES DE COMMANDE:
La faible consommation de courant PA-14P permet une connectivité avec la plupart de nos systèmes de commande. Pour plus d'informations sur nos boîtiers de commande plug-n-play et nos micro-contrôleurs, veuillez consulter notre page sur les systèmes de commande.
* Nos actionneurs PA-14P sont compatibles avec les boîtiers de commande PA-39 pour la possibilité d'enregistrer 3 emplacements prédéfinis, de contrôler les actionneurs linéaires en mouvement séquentiel et d'étendre, d'arrêter et de rétracter le mouvement. Pour plus d'informations, veuillez contacter sales@progressiveautomations.com.
Tableau de comparaison des actionneursOptions sur mesure
Vous recherchez un actionneur mais les spécifications ne correspondent pas exactement à ce dont vous avez besoin ? Nous avons une longue liste de capacités pouvant être faites sur mesure pour vous assurer d'obtenir exactement ce dont vous avez besoin pour votre projet. Téléchargez la fiche technique de ce produit et découvrez vos options sur mesure !
Le respect de normes est crucial pour notre entreprise afin de s'assurer que nos produits et services sont à un niveau de qualité qui garantie la satisfaction de la clientèle. Chez Progressive Automations, nous ne visons que le meilleur pour nos clients et nous nous continuons d'innover. Pour cette raison, nous sommes ravis d'annoncer que Progressive Automations est désormais certifié ISO 9001:2015 !
En savoir plusModèles 2D/3D

Modèles 3D
En fonction de votre application, vous devez tenir en compte différentes exigences techniques lors de la détermination de l' actionneur linéaire dont vous avez besoin. Ces exigences incluent la force, la course, la vitesse et les dimensions de fixation. Pour des informations détaillées sur l'actionneur, vous pouvez vous référer soit à la fiche technique, soit au tableau des spécifications situé sur la page produit de l'actionneur sélectionné. Vous pouvez également nous contacter pour parler avec l’un de nos ingénieurs experts.
Le cycle de service est la fraction de la période de travail pendant laquelle un actionneur linéaire peut rester actif. Vous pouvez calculer le cycle de service d'un actionneur linéaire à l'aide de l'équation suivante : Cycle de service (%) = (Durée pendant laquelle l'actionneur linéaire est actif) / (Durée d'une période de travail)
Par exemple : avec un cycle de service de 25 %, un actionneur peut fonctionner pendant 5 minutes en continu avant de devoir s'arrêter pendant 15 minutes avant de fonctionner.
La course est la distance de déplacement de la tige extensible. Pour trouver la longueur de course dont vous avez besoin, mesurez votre application de la position complètement rétractée à la position complètement déployée. La différence sera égale à la longueur de course dont vous avez besoin.
Nous recommandons toujours d'acheter un actionneur avec une force nominale supérieure à celle requise par l'application. Si vous n'êtes pas sûr de vos besoins en force, cet article peut vous aider à calculer ceci : Comment calculer la force pour trouver le bon actionneur linéaire
Oui, c'est possible. Cependant, cela dépend des unités que vous utilisez. Pour synchroniser les actionneurs, ils nécessitent une forme de rétroaction telle qu'un potentiomètre ou des capteurs à effet Hall. Pour plus d'informations, consultez ci-dessous certains de nos contenus clés concernant la synchronisation des actionneurs linéaires.
Contrôler plusieurs actionneurs linéaires en même temps
Comment utiliser les boîtiers de commande FLTCON-2 et FLTCON-4 ?
Le boîtier de commande que vous choisissez doit être capable de fournir une tension et un courant suffisants à votre actionneur. Si vous n'êtes pas sûr des spécifications, veuillez nous contacter .
Vous pouvez également trouver des boîtiers de commande compatibles sur la page produit de votre actionneur linéaire sélectionné.
Le retour en arrière se produit lorsqu'un actionneur commence à glisser sous une charge, lorsqu'il est surchargé ou lorsque l'actionneur a été endommagé. Voir la vidéo.
Que signifient les valeurs de charge dynamique et statique ?La charge nominale dynamique est la quantité de poids qu'un actionneur peut tirer ou pousser en toute sécurité lorsqu'il est alimenté. La charge statique est le poids que l'actionneur peut supporter ou supporter sans reculer lorsqu'il n'est pas alimenté. Par exemple, disons simplement que vous avez un actionneur installé sur une fenêtre et que la charge statique de l'actionneur est de 100 lb, il pourrait subir un retour en arrière en cas de vent fort, ce qui signifie qu'il y aura plus de pression exercée sur l'actionneur, ce qui dépasser la charge nominale de 100 lb de l’actionneur.
Qu’est-ce que le chargement latéral ?Le chargement latéral se produit lorsque l'actionneur subit des forces latéralement. Les actionneurs ne sont pas du tout destinés à gérer les forces latérales, donc s'ils subissent des forces latérales, ils seront endommagés ou la pliera. Il est donc conseillé de ne jamais utiliser de forces latérales et de toujours s'assurer que l'actionneur est entièrement aligné ou synchronisé avec votre application, afin qu'il ne supporte aucune charge autre que la charge axiale. Voir la vidéo.