Different stroke lengths of models are available upon request, please email us at: sales@progressiveautomations.com
This example code uses a MegaMoto Plus and an Arduino Uno to monitor the current of a linear actuator, however, similar products can be used as substitutions.
/* Code to monitor the current amp draw of the actuator, and to cut power if it
rises above a certain amount.
Written by Progressive Automations
August 19th, 2015
Hardware:
- RobotPower MegaMoto control boards
- Arduino Uno
- 2 pushbuttons
*/
const int EnablePin = 8;
const int PWMPinA = 11;
const int PWMPinB = 3; // pins for Megamoto
const int buttonLeft = 4;
const int buttonRight = 5;//buttons to move the motor
const int CPin1 = A5; // motor feedback
int leftlatch = LOW;
int rightlatch = LOW;//motor latches (used for code logic)
int hitLimits = 0;//start at 0
int hitLimitsmax = 10;//values to know if travel limits were reached
long lastfeedbacktime = 0; // must be long, else it overflows
int firstfeedbacktimedelay = 750; //first delay to ignore current spike
int feedbacktimedelay = 50; //delay between feedback cycles, how often you want the motor to be checked
long currentTimefeedback = 0; // must be long, else it overflows
int debounceTime = 300; //amount to debounce buttons, lower values makes the buttons more sensitive
long lastButtonpress = 0; // timer for debouncing
long currentTimedebounce = 0;
int CRaw = 0; // input value for current readings
int maxAmps = 0; // trip limit
bool dontExtend = false;
bool firstRun = true;
bool fullyRetracted = false;//program logic
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(EnablePin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PWMPinA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PWMPinB, OUTPUT);//Set motor outputs
pinMode(buttonLeft, INPUT);
pinMode(buttonRight, INPUT);//buttons
digitalWrite(buttonLeft, HIGH);
digitalWrite(buttonRight, HIGH);//enable internal pullups
pinMode(CPin1, INPUT);//set feedback input
currentTimedebounce = millis();
currentTimefeedback = 0;//Set initial times
maxAmps = 15;// SET MAX CURRENT HERE
}//end setup
void loop()
{
latchButtons();//check buttons, see if we need to move
moveMotor();//check latches, move motor in or out
}//end main loop
void latchButtons()
{
if (digitalRead(buttonLeft)==LOW)//left is forwards
{
currentTimedebounce = millis() - lastButtonpress;// check time since last press
if (currentTimedebounce > debounceTime && dontExtend == false)//once you've tripped dontExtend, ignore all forwards presses
{
leftlatch = !leftlatch;// if motor is moving, stop, if stopped, start moving
firstRun = true;// set firstRun flag to ignore current spike
fullyRetracted = false; // once you move forwards, you are not fully retracted
lastButtonpress = millis();//store time of last button press
return;
}//end if
}//end btnLEFT
if (digitalRead(buttonRight)==LOW)//right is backwards
{
currentTimedebounce = millis() - lastButtonpress;// check time since last press
if (currentTimedebounce > debounceTime)
{
rightlatch = !rightlatch;// if motor is moving, stop, if stopped, start moving
firstRun = true;// set firstRun flag to ignore current spike
lastButtonpress = millis();//store time of last button press
return; }//end if
}//end btnRIGHT
}//end latchButtons
void moveMotor()
{
if (leftlatch == HIGH) motorForward(255); //speed = 0-255
if (leftlatch == LOW) motorStop();
if (rightlatch == HIGH) motorBack(255); //speed = 0-255
if (rightlatch == LOW) motorStop();
}//end moveMotor
void motorForward(int speeed)
{
while (dontExtend == false && leftlatch == HIGH)
{
digitalWrite(EnablePin, HIGH);
analogWrite(PWMPinA, speeed);
analogWrite(PWMPinB, 0);//move motor
if (firstRun == true) delay(firstfeedbacktimedelay); // bigger delay to ignore current spike
else delay(feedbacktimedelay); //small delay to get to speed
getFeedback();
firstRun = false;
latchButtons();//check buttons again
}//end while
}//end motorForward
void motorBack (int speeed)
{
while (rightlatch == HIGH)
{
digitalWrite(EnablePin, HIGH);
analogWrite(PWMPinA, 0);
analogWrite(PWMPinB, speeed);//move motor
if (firstRun == true) delay(firstfeedbacktimedelay);// bigger delay to ignore current spike
else delay(feedbacktimedelay); //small delay to get to speed
getFeedback();
firstRun = false;
latchButtons();//check buttons again
}//end while
dontExtend = false;//allow motor to extend again, after it has been retracted
}//end motorBack
void motorStop()
{
analogWrite(PWMPinA, 0);
analogWrite(PWMPinB, 0);
digitalWrite(EnablePin, LOW);
firstRun = true;//once the motor has stopped, reenable firstRun to account for startup current spikes
}//end stopMotor
void getFeedback()
{
CRaw = analogRead(CPin1); // Read current
if (CRaw == 0 && hitLimits < hitLimitsmax) hitLimits = hitLimits + 1;
else hitLimits = 0; // check to see if the motor is at the limits and the current has stopped
if (hitLimits == hitLimitsmax && rightlatch == HIGH)
{
rightlatch = LOW; // stop motor
fullyRetracted = true;
}//end if
else if (hitLimits == hitLimitsmax && leftlatch == HIGH)
{
leftlatch = LOW;//stop motor
hitLimits = 0;
}//end if
if (CRaw > maxAmps)
{
dontExtend = true;
leftlatch = LOW; //stop if feedback is over maximum
}//end if
lastfeedbacktime = millis();//store previous time for receiving feedback
}//end getFeedback
This example code shows how to control up to 4 of our linear actuators with the Arduino Uno and LC-82 MultiMoto Arduino Shield, however, similar products can be used as substitutions. This code is only meant for use with actuator models within the current limitations on each channel of the MultiMoto such as the PA-14 and PA-14P.
/* Example code to control up to 4 actuators, using the Robot Power MultiMoto driver.
Hardware:
- Robot Power MultiMoto
- Arduino Uno
Wiring:
- Connect actuators to the M1, M2, M3, M4 connections on the MultiMoto board.
- Connect the negative (black) to the right connection, positive (red) to the left.
- Connect a 12 volt source (minimum 1A per motor if unloaded, 8A per motor if fully loaded)to the BAT terminals. Ensure that positive and negative are placed in the correct spots.
Code modified by Progressive Automations from the example code provided by Robot Power
<a href="http://www.robotpower.com/downloads/" rel="nofollow"> http://www.robotpower.com/downloads/</a>
Robot Power MultiMoto v1.0 demo
This software is released into the Public Domain
*/
// include the SPI library:
#include <SPI.h>
// L9958 slave select pins for SPI
#define SS_M4 14
#define SS_M3 13
#define SS_M2 12
#define SS_M1 11
// L9958 DIRection pins
#define DIR_M1 2
#define DIR_M2 3
#define DIR_M3 4
#define DIR_M4 7
// L9958 PWM pins
#define PWM_M1 9
#define PWM_M2 10 // Timer1
#define PWM_M3 5
#define PWM_M4 6 // Timer0
// L9958 Enable for all 4 motors
#define ENABLE_MOTORS 8
int pwm1, pwm2, pwm3, pwm4;
boolean dir1, dir2, dir3, dir4;
void setup() {
unsigned int configWord;
// put your setup code here, to run once:
pinMode(SS_M1, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(SS_M1, LOW); // HIGH = not selected
pinMode(SS_M2, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(SS_M2, LOW);
pinMode(SS_M3, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(SS_M3, LOW);
pinMode(SS_M4, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(SS_M4, LOW);
// L9958 DIRection pins
pinMode(DIR_M1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(DIR_M2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(DIR_M3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(DIR_M4, OUTPUT);
// L9958 PWM pins
pinMode(PWM_M1, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(PWM_M1, LOW);
pinMode(PWM_M2, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(PWM_M2, LOW); // Timer1
pinMode(PWM_M3, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(PWM_M3, LOW);
pinMode(PWM_M4, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(PWM_M4, LOW); // Timer0
// L9958 Enable for all 4 motors
pinMode(ENABLE_MOTORS, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(ENABLE_MOTORS, HIGH); // HIGH = disabled
/ /******* Set up L9958 chips *********
' L9958 Config Register
' Bit
'0 - RES
'1 - DR - reset
'2 - CL_1 - curr limit
'3 - CL_2 - curr_limit
'4 - RES
'5 - RES
'6 - RES
'7 - RES
'8 - VSR - voltage slew rate (1 enables slew limit, 0 disables)
'9 - ISR - current slew rate (1 enables slew limit, 0 disables)
'10 - ISR_DIS - current slew disable
'11 - OL_ON - open load enable
'12 - RES
'13 - RES
'14 - 0 - always zero
'15 - 0 - always zero
*/ // set to max current limit and disable ISR slew limiting
configWord = 0b0000010000001100;
SPI.begin();
SPI.setBitOrder(LSBFIRST);
SPI.setDataMode(SPI_MODE1); // clock pol = low, phase = high
// Motor 1
digitalWrite(SS_M1, LOW);
SPI.transfer(lowByte(configWord));
SPI.transfer(highByte(configWord));
digitalWrite(SS_M1, HIGH);
// Motor 2
digitalWrite(SS_M2, LOW);
SPI.transfer(lowByte(configWord));
SPI.transfer(highByte(configWord));
digitalWrite(SS_M2, HIGH);
// Motor 3
digitalWrite(SS_M3, LOW);
SPI.transfer(lowByte(configWord));
SPI.transfer(highByte(configWord));
digitalWrite(SS_M3, HIGH);
// Motor 4
digitalWrite(SS_M4, LOW);
SPI.transfer(lowByte(configWord));
SPI.transfer(highByte(configWord));
digitalWrite(SS_M4, HIGH);
//Set initial actuator settings to pull at 0 speed for safety
dir1 = 0; dir2 = 0; dir3 = 0; dir4 = 0; // Set direction
pwm1 = 0; pwm2 = 0; pwm3 = 0; pwm4 = 0; // Set speed (0-255)
digitalWrite(ENABLE_MOTORS, LOW);// LOW = enabled
} // End setup
void loop() {
dir1 = 1;
pwm1 = 255; //set direction and speed
digitalWrite(DIR_M1, dir1);
analogWrite(PWM_M1, pwm1); // write to pins
dir2 = 0;
pwm2 = 128;
digitalWrite(DIR_M2, dir2);
analogWrite(PWM_M2, pwm2);
dir3 = 1;
pwm3 = 255;
digitalWrite(DIR_M3, dir3);
analogWrite(PWM_M3, pwm3);
dir4 = 0;
pwm4 = 128;
digitalWrite(DIR_M4, dir4);
analogWrite(PWM_M4, pwm4);
delay(5000); // wait once all four motors are set
dir1 = 0;
pwm1 = 128;
digitalWrite(DIR_M1, dir1);
analogWrite(PWM_M1, pwm1);
dir2 = 1;
pwm2 = 255;
digitalWrite(DIR_M2, dir2);
analogWrite(PWM_M2, pwm2);
dir3 = 0;
pwm3 = 128;
digitalWrite(DIR_M3, dir3);
analogWrite(PWM_M3, pwm3);
dir4 = 1;
pwm4 = 255;
digitalWrite(DIR_M4, dir4);
analogWrite(PWM_M4, pwm4);
delay(5000);
}//end void loop
This example code is for combining the Wasp single-channel speed controller with the Arduino Uno to control the motion of a linear actuator, however, similar products can be used as substitutions.
/*Sample code for the Robot Power Wasp.
This ESC is controlled using RC signals, with pulses
ranging from 1000 - 2000 microseconds.
The main loop of this program holds the actuator still for 1 second, extends for 2 seconds,
stops for 1 second, retracts for 2 seconds, and repeats.
Modified by Progressive Automations, using the original example code "Sweep" from the
Arduino example libraries.
Hardware:
- 1 Wasp Controller
- Arduino Uno
Wiring:
Control side:
- Connect the red/black to +5v and GND
- Connect the yellow wire to your signal pin on the Arduino (in this example, pin 9)
Power Side:
- Connect the +/- of the motors power supply to the +/- connections on the Wasp
- Connect the +/- of the actuator to the remaining two connections
This example code is in the public domain.
*/
#include <servo.h>
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
// twelve servo objects can be created on most boards
int pos = 0; // variable to store the servo position
void setup()
{
myservo.attach(9); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object
}
void loop()
{
myservo.writeMicroseconds(1500); // stop signal
delay(1000); //1 second
myservo.writeMicroseconds(2000); // full speed forwards signal
delay(2000); //2 seconds
myservo.writeMicroseconds(1500); // stop signal
delay(1000); // 1 second
myservo.writeMicroseconds(1000); // full speed reverse signal
delay(2000); //2 seconds
}
This example code utilizes our relays and Arduino Uno to control a linear actuator, however, similar products can be used as substitutions. You can read our full blog post for more detail.
const int forwards = 7;
const int backwards = 6;//assign relay INx pin to arduino pin
void setup() {
pinMode(forwards, OUTPUT);//set relay as an output
pinMode(backwards, OUTPUT);//set relay as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(forwards, LOW);
digitalWrite(backwards, HIGH);//Activate the relay one direction, they must be different to move the motor
delay(2000); // wait 2 seconds
digitalWrite(forwards, HIGH);
digitalWrite(backwards, HIGH);//Deactivate both relays to brake the motor
delay(2000);// wait 2 seconds
digitalWrite(forwards, HIGH);
digitalWrite(backwards, LOW);//Activate the relay the other direction, they must be different to move the motor
delay(2000);// wait 2 seconds
digitalWrite(forwards, HIGH);
digitalWrite(backwards, HIGH);//Deactivate both relays to brake the motor
delay(2000);// wait 2 seconds
}
This example code uses our LC-80, Arduino Uno, any linear actuator and a power source, however, similar products can be used as substitutions. You can get more detail on the code and what it does in our blog post.
//Use the jumpers on the board to select which pins will be used
int EnablePin1 = 13;
int PWMPinA1 = 11;
int PWMPinB1 = 3;
int extendtime = 10 * 1000; // 10 seconds, times 1000 to convert to milliseconds
int retracttime = 10 * 1000; // 10 seconds, times 1000 to convert to milliseconds
int timetorun = 300 * 1000; // 300 seconds, times 1000 to convert to milliseconds
int duty;
int elapsedTime;
boolean keepMoving;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(EnablePin1, OUTPUT);//Enable the board
pinMode(PWMPinA1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PWMPinB1, OUTPUT);//Set motor outputs
elapsedTime = 0; // Set time to 0
keepMoving = true; //The system will move
}//end setup
void loop() {
if (keepMoving)
{
digitalWrite(EnablePin1, HIGH); // enable the motor
pushActuator();
delay(extendtime);
stopActuator();
delay(10);//small delay before retracting
pullActuator();
delay(retracttime);
stopActuator();
elapsedTime = millis();//how long has it been?
if (elapsedTime > timetorun) {//if it's been 300 seconds, stop
Serial.print("Elapsed time is over max run time. Max run time: ");
Serial.println(timetorun);
keepMoving = false;
}
}//end if
}//end main loop
void stopActuator() {
analogWrite(PWMPinA1, 0);
analogWrite(PWMPinB1, 0); // speed 0-255
}
void pushActuator() {
analogWrite(PWMPinA1, 255);
analogWrite(PWMPinB1, 0); // speed 0-255
}
void pullActuator() {
analogWrite(PWMPinA1, 0);
analogWrite(PWMPinB1, 255);//speed 0-255
}
This program can be use to continuously extend and retract the stroke of a linear actuator.
SETUP LOOP CODE
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // initialize serial communication at 9600 bits per second
pinMode(out_lim, INPUT_PULLUP); // configures pin 45 as input pin
pinMode(in_lim, INPUT_PULLUP); // configures pin 53 as input pin
pinMode(run_f, OUTPUT); // configures pin 25 as output pin
pinMode(run_r, OUTPUT); // configures pin 30 as output pin
retract(); // retracts the stroke on startup
delay(500);
}
void extend() // this function enables the motor to run
{
digitalWrite(run_f, LOW);
digitalWrite(run_r, HIGH);
}
void retract() // this function reverses the direction of motor
{
digitalWrite(run_f, LOW);
digitalWrite(run_r, LOW);
}
void run_stop() // this function disables the motor
{
digitalWrite(run_f, HIGH);
digitalWrite(run_r, HIGH);
}
void loop() {
int out_lim_state = digitalRead(out_lim); // reads the limit switches and saves its value
int in_lim_state = digitalRead(in_lim);
Serial.print("outer limit switch value "), Serial.println(out_lim_state); // 0 -> limit switch is pressed
Serial.print("inner limit switch value "), Serial.println(in_lim_state); // 1 -> limit switch is not pressed
if (out_lim_state == 0 && in_lim_state == 1) // if outer limit switch is pressed and inner is not (extended all the way)
{
retract(); // retract the stroke
}
else if (out_lim_state == 1 && in_lim_state == 0) // if inner limit switch is pressed and outer is not (reracted all the way)
{
extend(); // extend the stroke
}
else // otherwise do nothing
{
}
delay(5); // delay in between reads for stability
}
We have data sheets, user manuals, 3D models, wiring diagrams and more in our Resources and Learning Center sections.
Depending on your application, there are different specification requirements you should consider when determining the linear actuator you need. These requirements include force, stroke, speed and mounting dimensions. For detailed actuator information, you can refer to either the datasheet or the specification table located on the selected actuator's product page. You can also contact us to speak with one of our expert engineers.
Duty cycle is the fraction of the working period in which a linear actuator can remain active. You can calculate the duty cycle of a linear actuator by using the following equation: Duty cycle (%) = (Time the linear actuator is active) / (Time for one working period)
For example: With a 25% duty cycle, an actuator can run for 5 minutes continuously before needing to rest for 15 minutes before operating.
Yes, our actuators can be seamless replacements for most applications. Please contact us if you are unsure of which actuator to opt for. You will need to know the voltage rating, force rating, and stroke length needed before we can give a recommendation for a replacement actuator.
Stroke is the travel distance of the extending rod. To find the stroke length you require, measure your application from the fully retracted position to the fully extended position. The difference will equal the stroke length you require.
We always recommend purchasing an actuator with a higher force rating than what the application requires. If unsure of your force requirements, this article may help you calculate this: How to Calculate Force to Find the Right Linear Actuator
Yes. However, it is important to have sufficient voltage and current to be applied to your actuator. Here is an article that may help you further: How to Choose the Right Power Supply for your Linear Actuator
To achieve synchronous motion control, you will require feedback. We offer feedback in the forms of internal limit switches, potentiometers, or hall effect sensors. The following article highlights some Progressive Automations' products that can be used for synchronized control: Controlling Multiple Linear Actuators at the Same Time
There are a number of reasons your linear actuator may be exerting a large amount of noise including over-force, side loading or potential water infiltration. However, it may also be the case that your actuator is simply a high-force rated actuator and therefore has a loud operating noise level. For information on how to possibly overcome this loud noise, please click here. If you are concerned there may be an issue with your actuator, please contact us.
Most of our linear actuators are available for customization. Please refer to your desired product’s datasheet to view the full capabilities of its custom options. Please note there will be a lead time of approximately 20 – 25 business days for production, excluding shipping time. There will also be an additional fee for each actuator that is modified. To find out more about custom orders, please contact us at 1800 – 676 – 6123.
Yes, this is possible. However, it does depend on the units you are currently using. To synchronize actuators, they require a form of feedback such as a potentiometer or hall effect sensors. For more information, see below some of our key content regarding linear actuator synchronization.
Presently, we do not have kits available. However, if you would like a recommendation on the compatibility of certain linear actuators with control systems, please email us at sales@progressiveautomations.com with the following information:
• Required voltage rating
• Required stroke length
• Required force rating
• Dimensional limitations of your application
• Description of your application into which the actuator(s) will be installed
Temperature may be a factor in the functionality of your linear actuator. Please ensure that you use your actuator within the specifications advised in the product datasheet. If you have a specific query related to an actuator and temperature, please contact us.
To do this, please ensure the specifications for your system are compatible with the actuator’s voltage and current ratings. If these specifications align with each other, this may be possible. Please contact us if you are unsure of which actuator to opt for.
To find this information please refer to your product’s data sheet. If your linear actuator was customized, please provide us with images of the product, including your sales order number (if possible) and email this information to sales@progressiveautomations.com
Please click here for a list of 3D CAD models available.
The control box you choose should be able to provide sufficient voltage and current rating to your actuator. If you are unsure of the specifications, please contact us.
Alternatively, you can also find compatible control boxes on your selected linear actuator's product page.
To do this, please ensure the specifications for your system are compatible with the control box’s voltage and current ratings. If these specifications align, this may be possible. if you are unsure of their compatibility, please contact us.
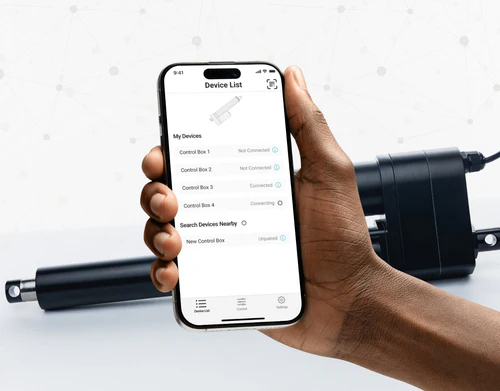
Yes, our PA-35 can control up to four linear actuators using an android/iOS device. For more information, read our detailed article on how to use our Wi-Fi control box and App.
No. However, we have a large variety of control boxes to choose from for each actuator. Alternatively, you may also use rocker switches as a form of motion control.
Yes, however you need to ensure your control box can provide sufficient current draw and compatible voltage. Otherwise, you risk damaging your actuator(s).
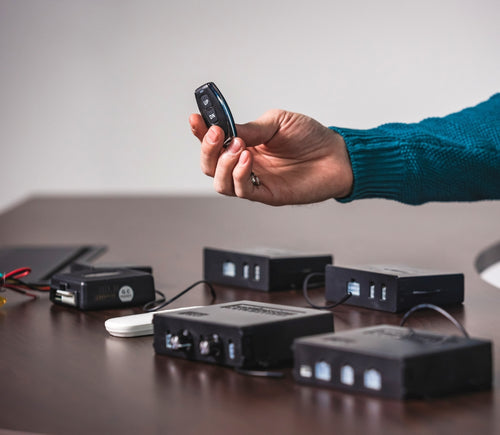
As we are primarily manufacturers and distributors, we have a limited amount of sample codes available. While we cannot provide specific coding for your application, we do have a growing list of sample Arduino codes. To access these sample codes, please click here.
We have a range of AC to DC power supplies to choose from in our catalog. As the majority of our actuators are powered via 12 VDC, a 12 VDC automotive battery is also a good solution. Please ensure the connected devices will provide sufficient current to your setup.
You can use your own power supply if it provides sufficient current draw and the right voltage to your system. Otherwise, you run the risk of damaging your actuator(s) and/or control box(es).
Yes, most of our power supplies can be converted up to 230 VAC. To browse our power supply range, click here.
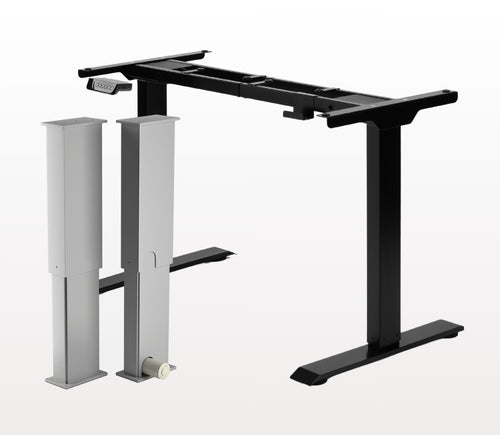
While possible, we recommend using the control box that is included with the lifting column sets. These control boxes are specifically programmed for the lifting columns to work in synchronous motion and using a third-party controller may compromise this.
However, our new LG-11 offers many similar characteristics to the FLT-11 and has the option to be paired with the FLTCON series of control boxes and RT-11 remote for multiple units to travel in synchronous motion. We do have dual lifting column systems available such as FLT-06 or FLT-10 that could provide you with a minimum height of 22 inches from the ground.
All of our lifting columns include control boxes and remotes to control the units. If you would like to know more about the control boxes we use, please contact us.
The only customizable feature for our table/TV lifts is the input voltage. Please note that there will be a lead time of 20 – 25 business days for production of all custom orders.
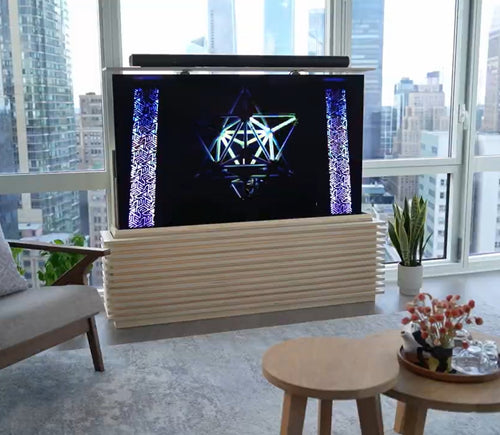
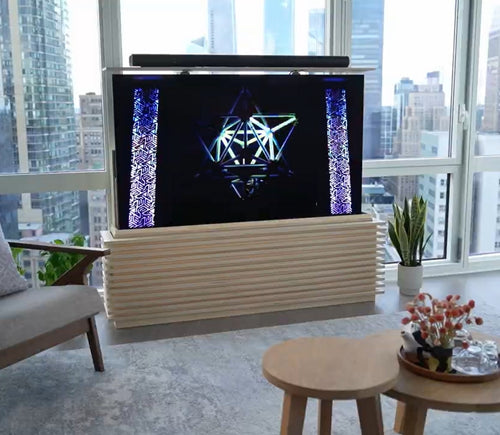
Our motorized pop-up TV lift is capable of holding up to 60-inch TV’s and our drop-down TV lifts can cater for up to 95-inch TV’s. Click here to browse our TV lifts. For even more information, check out our guide to using TV lifts.
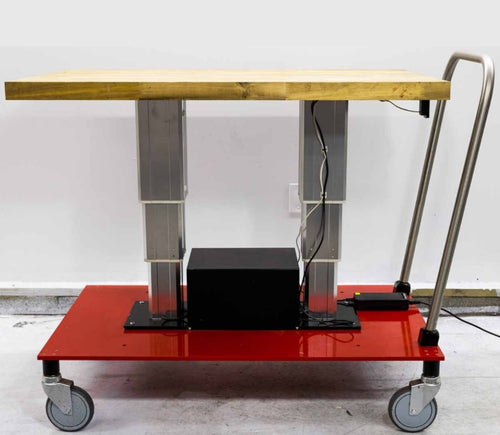
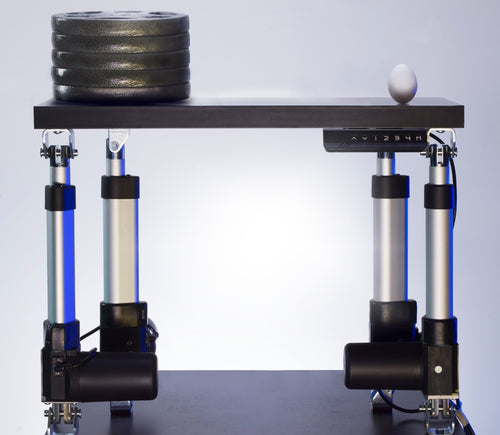
Our table lift weight capacities are dependent on the unit you are choosing. The minimum weight capacity in our line of table lifts is 180 lbs (equal to approximately 80 kg) for our FLT-01 Single Table Lift. The maximum weight capacity in our line of table lifts is 330 lbs (equal to approximately 150 kg) for our FLT-09 Table Lift Set and FLT-05 Table Lift Set.
No, all of our mounting brackets are sold separately to our linear actuators. However, we do produce compatible mounting brackets for each of our linear actuators. To find out which mounting bracket is suitable for your linear actuator, check out your selected actuator's product page (where it will be stated), or browse our mounting bracket catalog.
For this information, please refer to our wiring diagrams.
Please email us photos of your wiring setup so we can look into this further for you. One of our sales engineers will contact you as soon as possible.
Selecting the right electric actuator for your application is a key part of bringing it to life. You need to ensure it meets all your specifications and has the ability to do exactly what you want it to do. That is why we created this handy little flowchart for selecting a linear actuator. It is broken down into four sections, with each section showing different options for our actuators so you can clearly see how they differentiate from each other:

Backdriving is when an actuator starts sliding down under load, when it is either overloaded or when the actuator has been damaged. Watch the video.
What Does Dynamic and Static Load Ratings Mean?Dynamic load rating is the amount of weight an actuator can pull or push safely when being powered. Static load rating is the amount of weight the actuator can hold or withstand without back driving when it is not being powered. For example, let's just say you have an actuator installed on a window and the static load rating of the actuator is 100lbs, it could experience backdriving when there is a high wind event, which means there will be more pressure exerted on the actuator which would exceed the 100lbs load rating of the actuator.
What Is Lateral Loading?Lateral loading is when the actuator experiences forces from the lateral plane. Actuators are not meant to handle lateral forces at all so if it experiences any lateral forces, it will likely damage the actuator or bend the rod. So it's advised never to use lateral forces and always make sure the actuator is fully in line or in sync with your application, so it does not take any load other than the axial load. Watch the video.
Orders can be placed by one of the following ways:
Online: Use our online order process with options to pay by Credit Card or PayPal.
Phone: 1-800 – 676 – 6123
Yes, quantity discounts are applied if you purchase 7 or more of the same product. Quantity discount breakdowns are found on each product page. For more information on our discount structure please contact us.
We accept all major credit cards, PayPal, checks and wire transfers. For customers who wish to set up Net Term accounts, please email us to begin the application process.
For pricing in USD, please ensure you are visiting us from our US site. For pricing in CAD, please ensure you are visiting us from our Canadian site.
All products listed on the website are in stock and available for same-day shipping if your order is placed before 3pm PST. If one of our products is unavailable, we will contact you as soon as possible to inform you when the unit will be available.
Progressive Automations’ shipping fees are calculated based on a variety of factors including but not limited to: location, quantities, and the total weight of your order. Smaller items are shipped via parcel while larger items and bulk orders are shipped via a freight carrier service. We always endeavor to provide competitive shipping prices for all our customers.
Shipping methods are available through online and phone orders. If you wish to receive an estimated shipping cost of your order, this can be done by reviewing your final shopping cart.
We ship via multiple courier companies including FedEx, UPS, DHL and USPS. Your selected courier may vary based on your location. Any large orders are shipped using various freight forwarding companies.
Please contact us if you have any questions about these options or if you would like to ship using a different carrier/your own shipping account.
Canadian and USA customers will not pay or incur any duty taxes on their orders. Customers outside North America may be subject to duty and import fees. Please contact your local government authority for information on import fees and taxes.
Returns or exchanges are accepted within 30 days of receiving your order as long as the product has not been used, modified or damaged. For more information on our return policy please see our Shipping & Returns section.
Delivery to the continental United States may take between 4 to 10 business days. All other deliveries may take approximately 10 to 15 business days depending on your location. Please refer to our shipping policy for more information: Shipping & Returns
Unfortunately, Progressive Automations does not offer free shipping. However, you can get a quantity order discount starting at 7 of the same unit.
Yes, the L shaped standing desk is orientation-friendly and can be installed by your preference. Here is a step-by-step article that explains how this is possible: FLT-05 User Manual
NOTE: The steps below may vary depending on the remote model that you have. The following instructions were made for the standard RT-11 remote. To set the maximum height for your frame, go to the desired height you would like to set and follow the steps below:
- Press M and see [5 -] indicated on the display
- Press the UP button and notice [5 -] blinks
- Hold the M button until you see [999] on the display
- The maximum height has now been set
To set the minimum height for your frame, go to the desired height you would like to set and follow the steps below:
- Press M and see [5 -] indicated on the display
- Press the DOWN button and notice [5 -] blinks
- Hold the M button until you see [000] on the display
- The minimum height has now been set
To reset the limits, follow the steps below:
- Press M and see [5 -] indicated on the display and release
- Hold the M you see [555]
- Limits have been reset
NOTE: The steps below may vary depending on the remote model you have. The following instructions were made for the standard RT-11 remote.
If you have to hold down the remote’s buttons to get to your pre-set height, this means that your control box is in momentary control. To set your remote to non-momentary mode, follow the steps below
- Make sure that there is nothing underneath your desk, as we have to enter the reset procedure
- Press and hold the DOWN button until the display shows [ASr]
- Once [ASr] is shown, press and hold down [1] and you may see two values:
a. 10.1 = Non-momentary Mode
b. 10.2 = Momentary Mode
- Complete the reset procedure by holding the DOWN button until your standing desk slightly lowers and rises.
Our standing desks have 3 settings for collision detection, and this can be set depending on your preference. To proceed, follow the steps below:
- Make sure that there is nothing underneath your desk as we have to enter the reset procedure
- Press and hold the DOWN button until the display shows [ASr]
- Once [ASr] is shown, press and hold the UP [ ^ ] button and you may see three values:
a. 10.5 = 11 lbs
b. 10.6 = 22 lbs
c. 10.7 = 33 lbs
- Complete the reset procedure by holding the DOWN button until your standing desk slightly lowers and rises.
We have some troubleshooting steps for you to take if you see any of the following error codes on the frames with FLTCON series control boxes:
Сheck the error code here.
If the issue you are experiencing persists after following these steps, please feel free to contact our technical product engineers at 1-800-676-6123, or send us an email at sales@progressiveautomations.com.